What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease isn’t something that only happens to older people. Teens can get it too. Gum disease, also known as periodontal (pronounced: pair-ee-oh-DON-tul) disease, can cause problems from bad breath to pain and tooth loss.
Periodontal disease is inflammation of the gums. Gums are part of the mouth’s soft tissue. They surround and support the teeth and, when healthy, look pink and firm. Untreated gum disease can become very serious, causing teeth to become loose or fall out.
Did you know that gum disease if left untreated can cause gum recession, tooth loss, and can also be linked to heart disease as well as diabetes?
Some habits or factors can increase your risk of a periodontal disease:
● Smoking and substance abuse
● High levels of stress
● HIV and other chronic health problems
● Puberty or hormonal instability
● Diabetes and poor diet
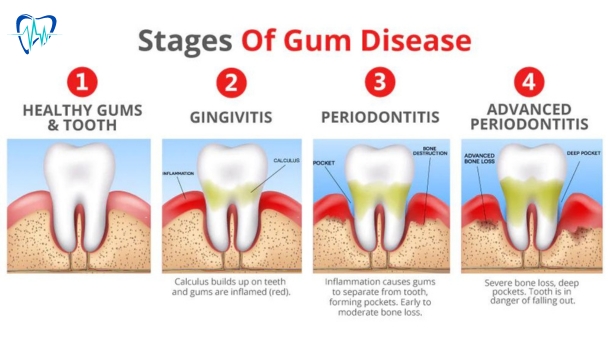
The Stages of Gum Disease
Gingivitis: The early stage of gum disease brought on by poor oral hygiene is gingivitis. It may not show any signs at all or it may make your gums swell, turn red, or bleed when you brush or floss. Before gingivitis worsens, it is essential to treat it.
Following gingivitis, periodontitis is the second stage of gum disease. When plaque penetrates beyond the gum line, it releases chemicals that cause a little amount of inflammation. Gum recession and widening gaps around the teeth are two apparent symptoms. If the infection is not adequately treated, it may also weaken the bone and cause your teeth to become loose.
Advanced Periodontitis: At this stage, the aforementioned symptoms worsen - teeth loosen further, bone loss continues and your gums swell as well. You may develop temperature sensitivity too.\
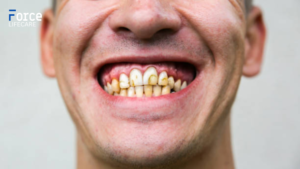
Symptoms of gum disease include:
Symptoms of gum disease can include:
- Swollen or puffy gums.
- Bright red, dark red or dark purple gums.
- Gums that feel tender when touched.
- Gums that bleed easily.
- A toothbrush that looks pink after brushing your teeth.
- Spitting out blood when brushing or flossing your teeth.
- Bad breath that won't go away.
- Pus between your teeth and gums.
- Loose teeth or loss of teeth.
- Painful chewing.
- New spaces that develop between your teeth that look like black triangles.
- Gums that pull away from your teeth, making your teeth look longer than usual, called receding gums.
- A change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite.
How Is Gum Disease Treated?
The treatment depends on the severity of the problem. The good news is that early stages of a gum disease like gingivitis is treatable and reversible, all you need is a good dental hygiene routine.
If plaque has hardened into tartar, and is below your gumline, you would need professional cleaning. Ideally your oral care expert would advise scaling and root planing (SRP). You can think of it as a deep clean procedure for your teeth, which helps fight the gum disease.
However, If the gum disease has been left neglected for some time, you might need other treatments to remove the damaged tissue or help reverse bone loss. In extreme cases, surgical or restorative interventions are a must.
The first step however is to get a thorough annual periodontal assessment and diagnosis. 'The right person to help with this is a periodontist - a dentist who specializes in preventing, diagnosing, and also treating gum disease.
Gum Disease Prevention
GUM DISEASE PREVENTION TIPS
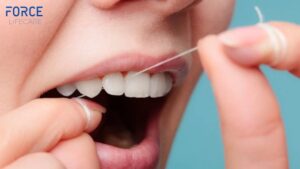
#1. FLOSS
Flossing is one of the most important things people can do to prevent gum disease. It is important to take the floss all the way down along the line of the tooth to remove any plaque from between the area of the tooth and actual gum. Most people make the mistake of stopping where the gum line begins. The lower portion of the tooth can trap plaque and cause tartar build-up as well. Thus, cleaning it out on a daily basis is necessary for true gum disease prevention.
For anyone who does not like to use traditional floss, floss picks can be used and these are a convenient tool that can be held in the hand and easily moved in between the tooth and gum.Some people even carry a flossing pick with them so that it can be used for lunches and snacks.
#2. AVOID DANGEROUS FOODS
Some foods and drinks are bad for oral health and that includes being bad for the gums. Stay away from sugar, candy, processed foods and anything acidic. These foods can have negative implications when it comes to oral health.
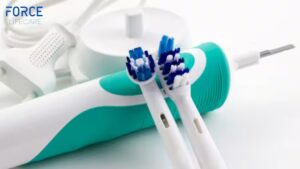
#3. USE A SOFT TOOTHBRUSH
When a toothbrush is too hard or abrasive, it can actually damage the gums and cause them to recede. Gum tissue is incredibly sensitive so using a hard toothbrush on a daily basis can cause the gums to inflame, bleed and begin to recede from the tooth structure. This can also increase the likelihood of gum disease forming. Thus, it is important to switch to an electric toothbrush or one that is soft.
#4 BRUSH FOR TWO MINUTES
Patients need to brush teeth for a full two minutes at a time, twice per day. Regular brushing ensures that the teeth and gums get a good clean and that plaque does not remain on the tooth structure. Patients need to complete this routine every day for life.
#5. AVOID TOBACCO USE OR EXCESSIVE ALCOHOL USE
It is also important not to drink alcohol in excess, smoke or chew tobacco. These things can be bad for health overall but are particularly dangerous for oral health.
Dental check-ups
It's important to have regular dental check-ups so any problems with your teeth and gums can be detected and treated early.
If you've never had gum disease and have good oral health, you may only need to visit your dentist every one to two years for a check-up.
You may need to visit your dentist more frequently if you've had problems with gum disease in the past. At each appointment your dentist will advise when you need your next appointment.
If you have an increased risk of developing gum problems – for example, if you smoke or have diabetes – you may be advised to visit your dentist more often so your teeth and gums can be closely monitored.
FAQ
They are particularly useful because they have anti-inflammatory properties and help to reverse gum diseases. Sources of omega-3s include pistachios, macadamia nuts and sesame seeds. They also serve as excellent sources of nutrients too
Vitamin C. Vitamin C strengthens your gums and the soft tissue in your mouth.
Latest Post
- Buy Dental Floss Online at ForceLifeCare
- Buy Electric Toothbrushes Online at ForceLifeCare
- Facing Several Problems Teeth Cleaning
- Force-lifecare Best Option for Dental Checkups
- Why Force-lifecare is Different
- Why Force-lifecare for your Dental Solution?
Other Links




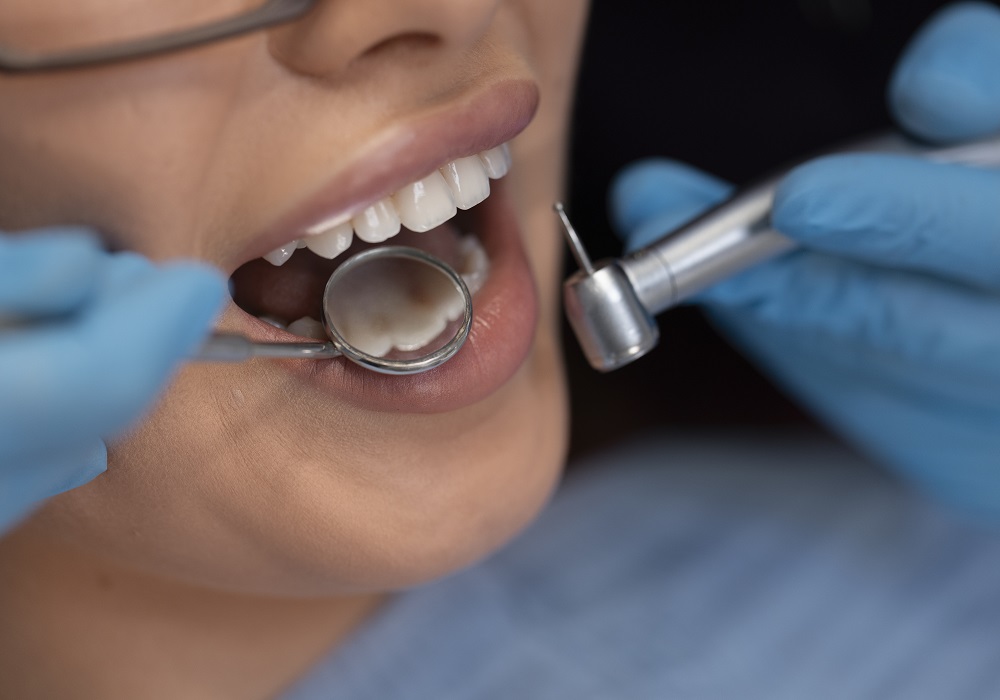 Dental Checkup Services
Dental Checkup Services
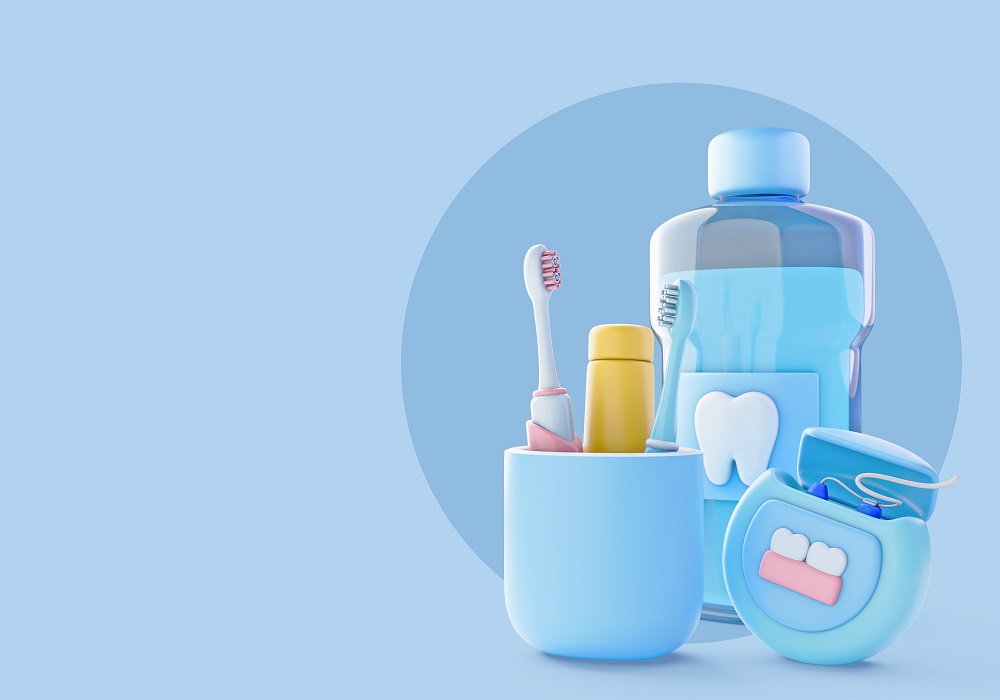 Our range of products
Our range of products
 Oral Care Blogs
Oral Care Blogs

Recent Comments